Understanding ISO 27001 Certification for Healthcare Organizations
In today’s digital age, healthcare organizations handle vast amounts of sensitive data, from patient medical records to financial information. Protecting this data is not only a legal requirement but also a crucial aspect of maintaining trust and operational integrity. This is where ISO 27001 Certification Services come into play. This certification is a globally recognized standard for information security management, providing a framework for managing and protecting sensitive information. For healthcare organizations, obtaining ISO 27001 certification is a strategic move to ensure robust data security, compliance, and patient trust.
What is ISO 27001 Certification?
ISO 27001 is an international standard for managing information security. It was published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) under the title “Information technology — Security techniques — Information Security Management Systems — Requirements”.The main objective of ISO 27001 is to assist organizations in protecting their information systematically and cost-effectively through the implementation of an Information Security Management System (ISMS). An ISMS provides a structured approach to managing sensitive company information, ensuring its security by involving people, processes, and IT systems, all governed by a comprehensive risk management process. For healthcare organizations, this involves protecting patient data, ensuring data integrity, and complying with legal and regulatory requirements.
Importance of ISO 27001 for Healthcare Organizations
Healthcare organizations are increasingly targeted by cyber-attacks due to the valuable data they hold. Personal health information is highly sensitive and can be used for identity theft, insurance fraud, and other malicious activities. Therefore, securing this information is of paramount importance.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Healthcare organizations must comply with various legal and regulatory requirements, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, and other national healthcare laws. ISO 27001 provides a framework that helps organizations comply with these regulations by implementing stringent data protection measures.
Risk Management: ISO 27001 helps healthcare organizations identify potential security risks and vulnerabilities and take proactive steps to mitigate them. This systematic approach to risk management ensures that all possible threats are considered and addressed.
Patient Trust: Maintaining patient trust is critical for healthcare organizations. Patients need to feel confident that their sensitive information is handled with the utmost care and security. ISO 27001 certification demonstrates a commitment to data protection, which can enhance patient trust and loyalty.
Operational Efficiency: Implementing ISO 27001 can lead to improved operational efficiency by streamlining processes and ensuring that information security is integrated into the daily operations of the organization. This can result in reduced incidents of data breaches and lower costs associated with data security management.
Steps to Achieve ISO 27001 Certification
Achieving ISO 27001 certification involves several steps, and while it may seem daunting, it is a worthwhile investment for healthcare organizations. Here is a detailed overview of the process:
Secure Management Support: The first step is to obtain commitment and support from top management. Without their backing, it is challenging to allocate the necessary resources and drive the project forward.
Define the Scope: Determine the scope of the ISMS. This involves identifying the areas of the organization that will be covered by the certification. For healthcare organizations, this typically includes all departments that handle patient data.
Conduct a Risk Assessment: Perform a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential security threats and vulnerabilities.This entails evaluating the probability and potential impact of various risks and prioritizing them according to their severity.
Develop a Risk Treatment Plan: Based on the risk assessment, develop a risk treatment plan that outlines the measures that will be implemented to mitigate identified risks. This may include technical controls, such as encryption and access controls, as well as procedural controls, such as policies and training.
Implement the ISMS: Implement the ISMS based on the risk treatment plan. This involves establishing policies, procedures, and controls to manage information security risks effectively. Ensure that all employees are trained and aware of their roles and responsibilities in maintaining information security.
Monitor and Review: Regularly monitor and review the ISMS to ensure its effectiveness. This includes conducting internal audits, reviewing incident reports, and assessing the performance of the implemented controls. Continuous improvement is a key aspect of ISO 27001.
External Audit and Certification: Once the ISMS is in place and functioning effectively, an external auditor will assess the system to determine if it meets the requirements of ISO 27001. If the auditor is satisfied, the organization will be awarded the ISO 27001 certification.
Key Components of ISO 27001
ISO 27001 encompasses various components that are essential for a robust ISMS. These include:
Information Security Policies: Develop and implement policies that outline the organization’s approach to managing information security.
Organization of Information Security: Establish a framework for managing information security within the organization, including roles and responsibilities.
Asset Management: Identify and manage information assets, ensuring that they are protected throughout their lifecycle.
Human Resource Security: Ensure that employees understand their information security responsibilities and are adequately trained.
Physical and Environmental Security: Implement measures to protect physical assets, such as servers and data centers, from unauthorized access and environmental threats.
Communications and Operations Management: Establish procedures for managing and securing the organization’s communication and operational processes.
Access Control: Implement controls to restrict access to sensitive information based on roles and responsibilities.
Information Systems Acquisition, Development, and Maintenance: Ensure that information security is considered during the acquisition, development, and maintenance of information systems.
Incident Management: Establish procedures for detecting, reporting, and responding to information security incidents.
Business Continuity Management: Develop and implement plans to ensure the continuity of critical business operations in the event of a security incident.
Challenges in Implementing ISO 27001 in Healthcare
While the benefits of ISO 27001 certification are significant, healthcare organizations may face several challenges during implementation.
Resource Constraints: Implementing ISO 27001 requires significant resources, including time, money, and personnel. Healthcare organizations may struggle to allocate these resources, particularly smaller facilities with limited budgets.
- Complexity of Healthcare Data: Healthcare data is often complex and diverse, including electronic health records (EHRs), medical images, and financial information. Managing and securing this data requires specialized knowledge and expertise.
- Cultural Resistance: Employees may resist changes to established processes and practices. Overcoming this resistance requires effective communication, training, and engagement from leadership.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating the ISMS with existing systems and processes can be challenging. This may require modifications to current workflows and IT systems, which can be disruptive and time-consuming.
- Keeping Up with Regulatory Changes: Healthcare organizations must stay abreast of constantly evolving legal and regulatory requirements. This requires ongoing monitoring and adjustments to the ISMS to ensure continued compliance.
Conclusion
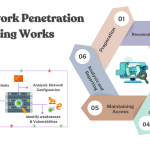
Network Penetration Testing stands as a critical pillar in modern information security services, offering organizations a proactive approach to identifying and mitigating cyber threats. Through a structured process encompassing preparation, reconnaissance, scanning, gaining access, maintaining access, analysis, and reporting, businesses can gain invaluable insights into their network’s vulnerabilities and security posture.
The diverse types of Network Penetration Testing, including Black Box, White Box, Gray Box, Internal, External, Targeted, and Social Engineering Testing, cater to various security needs, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of both internal and external threats.
Moreover, the adoption of advanced techniques such as exploitation frameworks, post-exploitation strategies, fileless attacks simulation, web application testing, cloud-based assessments, red team exercises, IoT and OT testing, and compliance testing elevates the effectiveness and relevance of penetration testing in today’s dynamic threat landscape.
Ultimately, Network Penetration Testing, coupled with advanced techniques, fosters a culture of continuous improvement, empowers organizations to make informed security decisions, and strengthens their defense strategies against evolving cyber threats. Embracing these practices is not just a proactive measure but a strategic imperative in safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining trust in the digital age.